
| 29
Chain Company
|
Drop Forging
THIELE
THIELE BIG-T
®
Chains
Chain Size
d x t [mm]
Article No. Test Force
kN
Elongation
under test force
% max.
Breaking Force
kN min.
Elongation at
fracture
%
Minimum
Defection
[mm]
34x121/131 F15505
1.090
1,4
1.450
11
34
42x140/152 F15506
1.660
1,4
2.220
11
42
48x144/158 F15501
2.170
1,4
2.900
11
48
52x156/171 F15502
2.550
1,4
3.400
11
52
56x168/184 F15503
2.960
1,4
3.940
11
56
60x181/197 F15504
3.390
1,4
4.520
11
60
Mechanical Properties
(THD)
the above values apply to chains in ‘natural black’ condition (NSW) / Technical specifcations subject to change
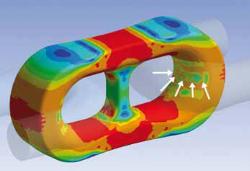
The newly developed two-point contact principle
of the Big-T chain allows the effective contact
area to be increased by distributing the contact
zone uniformly over the entire zone between the
two points. Contact pressure, and hence chain
wear, is therefore signifcantly reduced.
The vertical link is also broader and fatter in
design. This increase in width creates a much
larger wearing surface and provides increased
wear resistance, so that the overall wear
behaviour of the chain is very much improved.
The fatter design of this chain – which is even
fatter than the super-fat chain – makes it suita-
ble for use on extremely compact conveyors (for
low-seam applications*), or produces an
extremely strong and durable chain for a given
pan profle.
The round links have a fattened profle where
they engage with the bottom of the chain
pockets. This greatly improves the wear
behaviour of the chain on the sprocket.
The leg diameter d
1
is much smaller than the nominal diameter d – without any loss in chain performance.
The benefts include a 15% saving in weight at the round link and a larger volume of material at the critical
fight-bar profle, which signifcantly increases the stiffness and breaking force of the fight bar.
In spite of the broader contact face the smaller d
1
value means that the round link is also narrower than
that of a standard chain. The chain centre-to-centre spacing therefore remains unaltered, in spite of the
larger nominal size.